1. Introduction to EN 60204-1 Electrical Safety for Machinery
 EN 60204-1 outlines the general electrical safety requirements for machinery, with the goal of protecting both machinery operators and the equipment itself from electrical hazards. This standard is critical for reducing the risks associated with electrical systems in machines, particularly in industrial environments.
EN 60204-1 outlines the general electrical safety requirements for machinery, with the goal of protecting both machinery operators and the equipment itself from electrical hazards. This standard is critical for reducing the risks associated with electrical systems in machines, particularly in industrial environments.
Compliance with EN 60204-1 ensures that equipment is designed and maintained in a way that limits the risk of electrical shock, fire, and other hazards. This article will delve into some of the key aspects of electrical safety, including wire sizing, overcurrent protection, grounding, hazardous environments, shock protection, and fire protection.
2. Wire Sizing and Types
Wire sizing is a foundational aspect of electrical safety. Selecting the correct wire size is essential to prevent overheating, which can lead to insulation melting and fires.
Factors Affecting Wire Sizing
There are several factors to consider when determining the appropriate wire size for a machine:
- Current Capacity (Ampacity): Wires are rated for how much current they can safely carry. Exceeding this limit can cause the wire to overheat.
- Insulation Material: The insulation surrounding the wire plays a role in how much heat it can withstand before becoming compromised.
- Ambient Temperature: Higher temperatures may require a larger gauge wire to prevent excessive heating – this is related closely to the temperature rating of the insulation material.
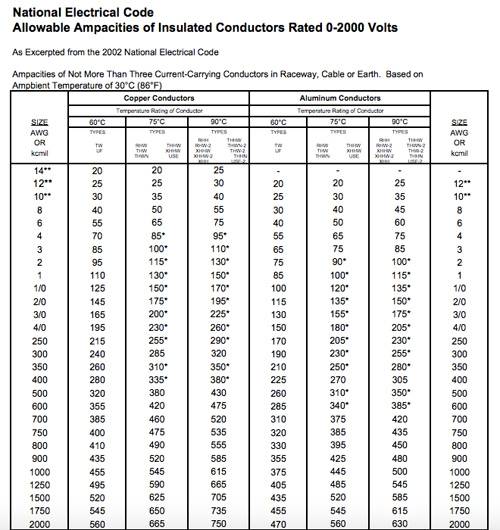
3. Overcurrent Protection Requirements
Overcurrent protection devices, such as fuses and circuit breakers, are critical for preventing damage to machinery and ensuring safety. These devices interrupt the flow of electricity when excessive current is detected, preventing overheating and potential fires.
Fuses and Circuit Breakers
- Fuses: A fuse contains a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, effectively breaking the circuit.
- Circuit Breakers: These are switch-like devices that open the circuit when excessive current is detected. Unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be reset after tripping.
Proper selection of fuses and breakers according to EN 60204-1 ensures that the machinery operates within safe current limits, avoiding electrical failures.
4. Grounding Requirements
Grounding is a fundamental component of electrical safety. It involves connecting part of the electrical system to the earth, providing a path for electric current to travel safely to the ground in case of a fault.
A proper grounding system is essential to protect users from electrical shocks. It also stabilizes voltage levels within the system, reducing the likelihood of equipment damage. Grounding is particularly important for large machines with metal parts that can become energized if there is a wiring issue.
5. Hazardous Environments and IP Ratings
Machines are often exposed to harsh environments where dust, moisture, or flammable materials may pose additional risks. To address these challenges, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) developed the IEC 60529 standard, which includes Ingress Protection (IP) ratings. These ratings indicate how resistant an enclosure is to dust and liquids, as well as the level of protection it provides against accidental contact with electrical parts.
Flammable Gases, Liquids, and Solids
Machines in hazardous environments must be specially designed to prevent the ignition of flammable substances. Key considerations include:
- Flammable Gases: Equipment should be housed in explosion-proof enclosures that prevent any sparks or electrical faults from igniting gas in the surrounding environment.
- Flammable Liquids: Machines should be designed with seals and barriers that prevent electrical sparks from coming into contact with flammable liquids.
- Flammable Solids: Electrical components should be isolated from dust or solid particles that can ignite in the presence of heat or sparks.
Dust Tightness and Weather Proofing
For machines in outdoor or dusty environments, IP ratings indicate the level of dust-tightness and weather resistance. For example, an IP67 rating indicates that the enclosure is completely dust-tight and can be submerged in water up to a certain depth.

6. Shock Protection
Electrical shock is one of the most common risks in machinery environments. EN 60204-1 outlines several ways to protect operators from shock hazards:
- Insulation: Proper insulation of electrical components reduces the risk of accidental contact with live wires.
- Enclosures: Machines should be equipped with enclosures that prevent access to dangerous electrical parts.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI): These devices automatically shut off power when they detect an imbalance in the electrical current, which could indicate a shock hazard.
Shock protection measures are especially important in environments where workers frequently interact with electrical machinery.
7. Fire Protection
Fires caused by electrical systems can result in extensive damage to machinery and surrounding infrastructure. EN 60204-1 includes provisions for fire-resistant construction and materials to mitigate the risk of fires spreading within machinery.
Fire-Resistance Ratings for Machinery
Flame resistance ratings vary by specific application and use case, however commonly utilized standards include:
UL94 (Underwriters Laboratories 94): This is specifically for evaluating the flammability of plastic materials used in devices and appliances. It includes classifications like HB (Horizontal Burning), V-0, V-1, and V-2, which indicate the material’s resistance to ignition and burning.
8. Conclusion
Electrical safety is a critical aspect of machinery design and operation. From selecting the correct wire size to ensuring proper grounding and fire protection, adhering to the guidelines set forth in EN 60204-1 helps reduce the risk of electrical hazards. Implementing these safety measures not only protects the machinery itself but also safeguards the people who operate and maintain it.
9. We’re here to answer your questions on Machinery Safety
Are you looking to ensure your machinery meets the highest standards of electrical safety? At Megalab Group Inc. we specialize in EN 60204-1 compliance testing and offer comprehensive electrical safety audits for all types of machinery. Our team of experts is ready to help you identify potential risks and implement solutions that keep your operations running smoothly.
Visit our Machinery Safety Service Page to learn more about how we can assist with your compliance needs, or contact us today for a consultation!
Got a Question?
We’re here to answer your questions and help you get started right away. Call or send us a message anytime.

Megalab Group
Megalab offers ISO 17025 A2LA Accredited, EMC, Product Safety, Mechanical & Laboratory Testing Services. Megalab Group Inc. and its team are committed to meet and exceed our customers’ expectations as an industry leader in environmental and related regulatory testing services, through constant business improvement while upholding the highest integrity and quality in standards of all services we provide.
Learn more at www.megalabinc.com


